Aggregate functions
SQL aggregate functions return a single value, calculated from values in a column.
Useful aggregate functions:
- AVG() - Returns the average value
- COUNT() - Returns the number of rows
- FIRST() - Returns the first value
- LAST() - Returns the last value
- MAX() - Returns the largest value
- MIN() - Returns the smallest value
- SUM() - Returns the sum
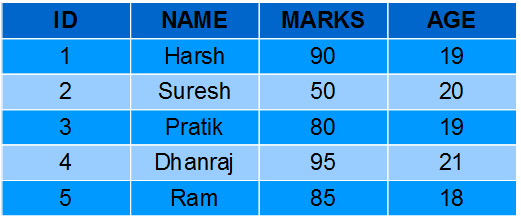
AVG(): It returns average value after calculating from values in a numeric column.
Syntax:
SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name;Queries:
Computing average marks of students.
SELECT AVG(MARKS) AS AvgMarks FROM Students;Output:
| AvgMarks | | :--- | | 80 |
Computing average age of students.
SELECT AVG(AGE) AS AvgAge FROM Students;Output:
| AvgAge | | :--- | | 19.4 |
COUNT(): It is used to count the number of rows returned in a SELECT statement. It can’t be used in MS ACCESS.
Syntax:
SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name;Queries:
Computing total number of students.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS NumStudents FROM Stuents;Output:
| NumStudents | | :--- | | 5 |
Computing number of students with unique/distinct age.
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT AGE) AS NumStudents FROM Students;Output:
| NumStudents | | :--- | | 4 |
FIRST():
The FIRST() function returns the first value of the selected column.
Syntax:SELECT FIRST(column_name) FROM table_name;Queries:
Fetching marks of first student from the Students table.
SELECT FIRST(MARKS) AS MarksFirst FROM Students;Output:
| MarksFirst | | :--- | | 90 |
Fetching age of first student from the Students table.
SELECT FIRST(AGE) AS AgeFirst FROM Students;Output:
| AgeFirst | | :--- | | 19 |
LAST(): The LAST() function returns the last value of the selected column. It can be used only in MS ACCESS.
Syntax:
SELECT LAST(column_name) FROM table_name;Queries:
Fetching marks of last student from the Students table.
SELECT LAST(MARKS) AS MarksLast FROM Students;Output:
| MarksLast | | :--- | | 82 |
Fetching age of last student from the Students table.
SELECT FIRST(AGE) AS AgeLast FROM Students;Output:
| AgeLast | | :--- | | 18 |
MAX(): The MAX() function returns the maximum value of the selected column.
Syntax:SELECT MAX(column_name) FROM table_name;Queries:
Fetching maximum marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT MAX(MARKS) AS MaxMarks FROM Students;Output:
| MaxMarks | | :--- | | 95 |
Fetching max age among students from the Students table.
SELECT MAX(AGE) AS MaxAge FROM Students;Output:
| MaxAge | | :--- | | 21 |
MIN(): The MIN() function returns the minimum value of the selected column.
Syntax:
SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
Fetching minimum marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT MIN(MARKS) AS MinMarks FROM Students;Output:
| MinMarks | | :--- | | 50 |
Fetching minimum age among students from the Students table.
SELECT MIN(AGE) AS MinAge FROM Students;Output:
| MinAge | | :--- | | 18 |
SUM(): The SUM() function returns the sum of all the values of the selected column.
Syntax:
SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
Fetching summation of total marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT SUM(MARKS) AS TotalMarks FROM Students;Output:
| TotalMarks | | :--- | | 400 |
Fetching summation of total age among students from the Students table.
SELECT SUM(AGE) AS TotalAge FROM Students;Output:
| TotalAge | | :--- | | 97 |