LEFT OUTER JOIN
Another type of join is called a SQL Server LEFT OUTER JOIN. This type of join returns all rows from the LEFT-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the joined fields are equal (join condition is met).
Syntax
The syntax for the LEFT OUTER JOIN in SQL Server (Transact-SQL) is:
SELECT columns FROM table1
LEFT [OUTER] JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column;
In some databases, the LEFT OUTER JOIN keywords are replaced with LEFT JOIN.
Visual Illustration
In this visual diagram, the SQL Server LEFT OUTER JOIN returns the shaded area:
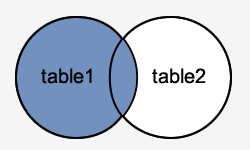
The SQL Server LEFT OUTER JOIN would return the all records fromtable1_and only those records from_table2_that intersect with_table1.
Example
Here is an example of a LEFT OUTER JOIN in SQL Server (Transact-SQL):
SELECT suppliers.supplier_id, suppliers.supplier_name, orders.order_date
FROM suppliers
LEFT OUTER JOIN orders
ON suppliers.supplier_id = orders.supplier_id;
This LEFT OUTER JOIN example would return all rows from the suppliers table and only those rows from the orders table where the joined fields are equal.
If a supplier_id value in the suppliers table does not exist in the orders table, all fields in the orders table will display as <null_>_in the result set.
Let's look at some data to explain how LEFT OUTER JOINS work:
We have a table called_suppliers_with two fields (supplier_id and supplier_name). It contains the following data:
| supplier_id | supplier_name |
|---|---|
| 10000 | IBM |
| 10001 | Hewlett Packard |
| 10002 | Microsoft |
| 10003 | NVIDIA |
We have a second table called_orders_with three fields (order_id, supplier_id, and order_date). It contains the following data:
| order_id | supplier_id | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| 500125 | 10000 | 2003/05/12 |
| 500126 | 10001 | 2003/05/13 |
Our result set would look like this:
| supplier_id | supplier_name | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| 10000 | IBM | 2003/05/12 |
| 10001 | Hewlett Packard | 2003/05/13 |
| 10002 | Microsoft | <null> |
| 10003 | NVIDIA | <null> |